Corel PaintShop Pro Help :
Adjusting images : Adjusting brightness, contrast, and clarity
Corel PaintShop Pro lets you adjust the brightness, contrast, and clarity in your photos. Contrast is the difference between the photo’s lightest and darkest pixels. Clarity lets you adjust the level of detail in the image by analyzing contrast within localized areas.
By applying the commands to a selection or an entire image, you can do the following:
Histograms
A histogram lets you display the tonal range of an image and redistribute the balance of highlights, midtones, and shadows. In other words, the histogram can reveal whether your photo is underexposed, overexposed, or exposed properly.
Many digital cameras offer a histogram display on the camera’s LCD, and some cameras even let you adjust the scene’s histogram before you take the photo.
Corel PaintShop Pro has various commands that display the histogram in the dialog box. These commands include Curves, Levels, the advanced mode of Smart Photo Fix, and Histogram Adjustment.
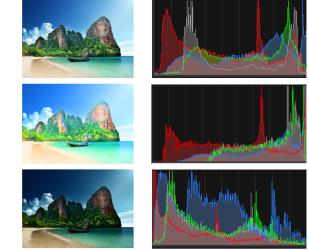
Example of histograms (right) for three different exposures.
Note the following when you look at a histogram:
The graph in the Histogram Adjustment dialog box displays the number of pixels for each value of the selected channel. The vertical axis represents the number of pixels and ranges from zero to the highest number of pixels in the graph. The horizontal axis represents the value of the selected channel, from 0 to 255.
You can display a Histogram for an image at any time by choosing View  Palettes
Palettes  Histogram.
Histogram.
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Brightness/Contrast. Brightness/Contrast. |
You can use the zoom control in the dialog box to set your view of the image in the Before and After panes.
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Fill Light/Clarity. Fill Light/Clarity. |
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Local Tone Mapping. Local Tone Mapping. |
You can use the zoom control in the dialog box to set your view of the image in the Before and After panes.
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Curves. Curves. |
|
2
|
In the Channel drop-list, select one of the following color channel options: |
|
• |
RGB — lets you edit the red, green, and blue channels in a combined histogram |
|
• |
Red — lets you edit the red channel only |
|
• |
Green — lets you edit the green channel only |
|
• |
Blue — lets you edit the blue channel only |
|
|
|
|
|
Note: Adding more points to the curve lets you adjust its shape more precisely.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Click the Contrast button in the Auto group box.
Note: You can use this button when you’re satisfied with the photo’s colors but want to improve the contrast.
|
|
|
Click the Color button in the Auto group box.
Note: You can use this button to find a black point and a white point in the photo automatically.
|
|
|
Click the Levels button in the Auto group box.
|
|
|
Click the black, gray, or white dropper in the Colors group box to activate the dropper color. Then, move the cursor into the Before pane and click what you know to be a black, gray, or white point.
The After pane (and the image window if the Preview on Image check box is marked) is updated.
|
|
|
Hold down Alt, and position the cursor in the Before pane (or in the image window). As you move the cursor over dark, medium, and light areas, the appropriate color dropper becomes active. Click to set that point.
|
Specify histogram clipping limits for the Auto Contrast, Color, and Levels buttons
|
Click the Options button. In the Auto Color Options dialog box, set percentage values for the Lower Limit and Upper Limit controls, and for the Strength control.
Note: For the Lower Limit and Upper Limit controls, higher values result in stronger automatic settings, and lower values result in weaker automatic settings. Lower Strength values result in less clipping.
|
|
|
Click the Reset button located near the Colors droppers.
You can also click the Reset to Default button located next to the Save Preset button.
|
You can use the zoom control in the dialog box to set your view of the image in the Before and After panes.
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Highlight/Midtone/Shadow. Highlight/Midtone/Shadow. |
|
• |
Absolute adjustment method — sets the absolute positions of the 25% histogram point (Shadows), the 50% histogram point (Midtones) and the 75% histogram point (Highlights). Typical values are about 35 for Shadow, 50 for Midtone, and 65 for Highlight, but they vary, depending on the photo. Increasing the value lightens the region, and decreasing the value darkens the region. |
|
• |
Relative adjustment method — adjusts the lightness levels relative to their original states. Positive values lighten the region, and negative values darken it. |
You can use the zoom control in the dialog box to set your view of the image in the Before and After panes.
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Histogram Adjustment. Histogram Adjustment. |
|
2
|
In the Edit group box, choose one of the following options: |
|
• |
Luminance — lets you set the lightness values of the image to correct contrast |
|
• |
Colors — lets you choose a color channel to edit |
|
3
|
In the Load Preset drop-list, choose Default. |
You can create artistic effects by using the Output Max and Output Min controls on the left side of the histogram. The Max slider is the white circle within a gray square; the Min slider is the black circle within a gray square. To darken the image’s lightest pixels, drag the Max slider down. To lighten the image’s darkest pixels, drag the Min slider up. Even though you are dragging sliders along the vertical axis, the Max and Min values (from 0 to 255) affect the horizontal axis. All pixels outside the range are converted so that they fall within the range. You can choose another color component from the Edit drop-list and make similar adjustments.
Edit workspace
| • |
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Histogram Equalize. Histogram Equalize. |
Edit workspace
| • |
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Histogram Stretch. Histogram Stretch. |
The Histogram Stretch command pulls the darkest pixel down to black and the lightest pixel up to white. This command does not affect images that already span from pure black to pure white. If the original image has pixels that are very close to black and white, using this command will have a very small effect. If the original image is very flat (nothing close to black or white), using this command will have a strong effect.
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Levels. Levels. |
|
2
|
In the Levels group box, choose the color channel to adjust from the Channel drop-list: |
|
• |
RGB — lets you edit the red, green, and blue channels in a combined histogram |
|
• |
Red — lets you edit the red channel only |
|
• |
Green — lets you edit the green channel only |
|
• |
Blue — lets you edit the blue channel only |
|
|
|
|
|
Click the Contrast button in the Auto group box.
Note: You can use this button when you’re satisfied with the photo’s colors but want to improve the contrast.
|
|
|
Click the Color button in the Auto group box.
Note: You can use this button to find a black point and a white point in the photo automatically.
|
|
|
Click the Levels button in the Auto group box.
|
|
|
Click the black, gray, or white dropper in the Colors group box to activate that dropper color. Then, move the cursor into the Before pane (or into the image window), and click what you know to be a black, gray, or white point.
The After pane (and the image window if the Preview on Image check box is marked) is updated.
|
|
|
Hold down Alt, and position the cursor in the Before pane (or in the image window). As you move the cursor over dark, medium, and light areas, the appropriate color dropper becomes active. Click to set that point.
|
Specify histogram clipping limits for the Auto Contrast, Color, and Levels buttons
|
Click the Options button. In the Auto Color Options dialog box, set percentage values for the Lower Limit and Upper Limit controls and for the Strength control.
Note: For the Lower Limit and Upper Limit controls, higher values result in stronger automatic settings, and lower values result in weaker automatic settings. Lower Strength values result in less clipping.
|
|
|
Click the Reset button located near the Colors droppers.
You can also click the Reset to Default button located next to the Save Preset button.
|
Changes you make in the Auto Color Options dialog box are applied when you use the Contrast, Curves, and Levels buttons in the Auto group box of the Curves dialog box.
You can use the Levels command to spread out the histogram for a photo taken with an improper exposure. You may find it helpful to use this command before using the Curves command.
You can use the zoom control in the dialog box to set your view of the image in the Before and After panes.
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Brightness and Contrast Brightness and Contrast  Threshold. Threshold. |
You can use the zoom control in the dialog box to set your view of the image in the Before and After panes.
Copyright 2013 Corel Corporation. All rights reserved.

![]() Palettes
Palettes ![]() Histogram.
Histogram.