Saturation is the purity or vividness of a color, expressed as the absence of white. A color with 100% saturation contains no white. A color with 0% saturation corresponds to a shade of gray. A hue is the property that defines a particular color. For example, blue, green, and red are all hues.
Hue refers to the actual color (such as red or yellow). Saturation is the vividness of the color. Imagine bright orange, which is a highly saturated color. As the saturation is reduced (keeping the hue and lightness unchanged), the orange color becomes brownish, then taupe, and finally a middle neutral gray (after the saturation has been reduced to zero). Reducing the saturation drains the color away, leaving just the grayscale component. Taupe and mauve are low-saturation colors because they are quite neutral, with just a touch of color. Apple red and banana yellow are high-saturation colors. Saturation is a measure of how different a color is from a neutral gray of the same brightness.
In digital images, increasing the saturation can give the image brilliant color and "punch," but too much saturation distorts colors and causes problems such as unnatural-looking skin tones. You can use the Vibrancy control to target only those areas that are low on saturation without affecting the rest of the image. For example, you can boost color in less saturated parts of an image without significantly altering skin tone.
Corel PaintShop Pro gives you four ways to alter the hue and saturation of a selection or of an entire image:
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Hue and Saturation Hue and Saturation  Colorize. Colorize. |
|
• |
Hue — specifies the hue to which all current colors are changed |
|
• |
Saturation — specifies the saturation of the selected hue |
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Hue and Saturation Hue and Saturation  Hue/Saturation/Lightness. Hue/Saturation/Lightness. |
|
2
|
In the Edit drop-list, do one of the following: |
|
The Hue value represents the change from the original pixel color as the number of degrees of rotation around the 360-degree color wheel. A positive value indicates a clockwise rotation, and a negative value indicates a counterclockwise rotation. For example, when the Hue value is 180, blue becomes yellow, and green becomes magenta. |
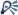
You can turn an image into a duotone (two-color) image by marking the Colorize check box, which converts the image to grayscale. To colorize the image, you can select a hue and adjust the saturation and lightness values.
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Hue and Saturation Hue and Saturation  Hue Map. Hue Map. |
|
Note: In the Hue Shift group box, the top row of color boxes shows 10 original colors, and the bottom row of color boxes shows the shifted colors. Each color is represented as degrees of rotation around the 360-degree color wheel. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In the Load Preset drop-list, choose Default.
|
Edit workspace
|
1
|
Choose Adjust  Hue and Saturation Hue and Saturation  Vibrancy. Vibrancy. |
Copyright 2013 Corel Corporation. All rights reserved.